What are the Types of Body Shapes?
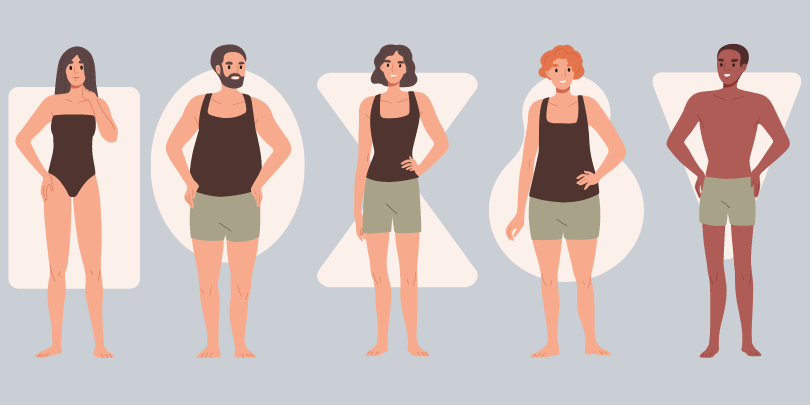

Bodies come in different shapes and sizes, influenced by a person’s frame and composition. Different body types can include triangle, rectangles, hourglass, ectomorphs, mesomorphs, and endomorphs. Different body types are part of what makes every human unique. Some bodies are curvier, some have broad shoulders, and some have more musculature. After puberty, a person’s body type is often established, however it might vary depending on their exercise level, food preferences, and other significant lifestyle and hormonal changes.
Types of Classification of Body Shapes:
- Ectomorph: This type of physique is slim, lean, and typically has less muscle and fat on it. Gaining weight in the form of fat or muscle might be difficult for those with this body type. One example of this body type is a fashion model.
- Endomorph: This type of person has a lot of muscle, stores more fat, and accumulates weight more quickly. Not everyone who has this body type is overweight. Examples of this body type are Marilyn Monroe and football linemen.
- Mesomorph: Strong and athletic bodies are referred to as mesomorphs. Underweight or overweight individuals make up this body type. One example of this body type is that of swimmers and volleyball players
Factors that determine a person’s body shape:
- Genetics
- Sex
- Age
- Diet
- Activity level
TYPES OF BODY SHAPES:
1. Rectangle Female Body Type
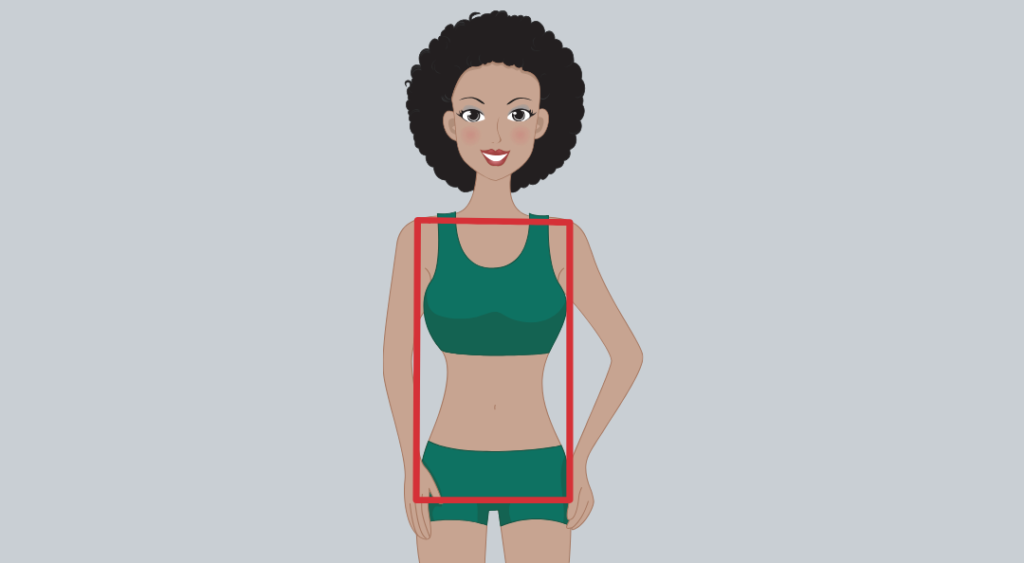

The rectangle female body type or often called the athletic build is the most upfront shape in the list. Rectangle body shape attributes:
- Your hips, waistline, and shoulders have about identical widths.
- Rectangles accumulate weight evenly but may accumulate some more through the upper body or neck.
- You have relatively straight shoulders.
- Your buttocks may appear to be flat.
- You have an athletic build and an undersized bustline.
Health Risk :
Many slender celebrities have this body type, but it doesn’t mean that all ruler-shaped people are skinny. If you are overweight, you are not exempt from a higher risk for heart disease and diabetes.
Women who are underweight are more susceptible to mental health issues, depression, menstrual issues, and difficulties becoming pregnant.
2. Inverted Triangle Female Body Type
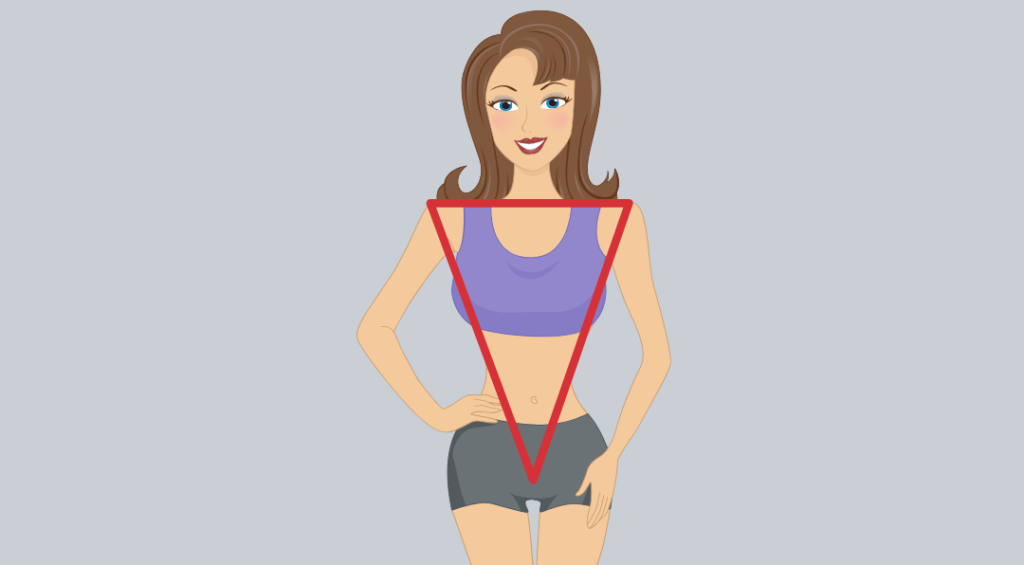
An inverted triangle body shape is expressed as a body shape with bigger proportions on the top than on the bottom. It also appears to be an athletic build as the legs and waist are quite smaller than the bust and shoulders’ width.
Inverted body shape attributes:
- You have distinguished and wide straight shoulders, broader than your waistline or hips.
- You have an athletic physique.
- You presumably have relatively flat buttocks.
- You might have a bigger chest and a more full back than rectangles.
- When inverted triangles accumulate weight, they usually accumulate it through the torso and back area.
Health Risk :
If you are a woman with a larger bust, you may have worried that your breast size could leave you at a higher risk for breast cancer. In fact, this link is unproven. Instead, you should have a better understanding of your breast density –– dense breasts have more connective tissue than fatty tissue, and can increase your risk for breast cancer. So, it’s not necessarily the size of the breast that puts you at risk for breast cancer. You can determine your breast density through regular mammograms.
3. Hourglass Female Body Type
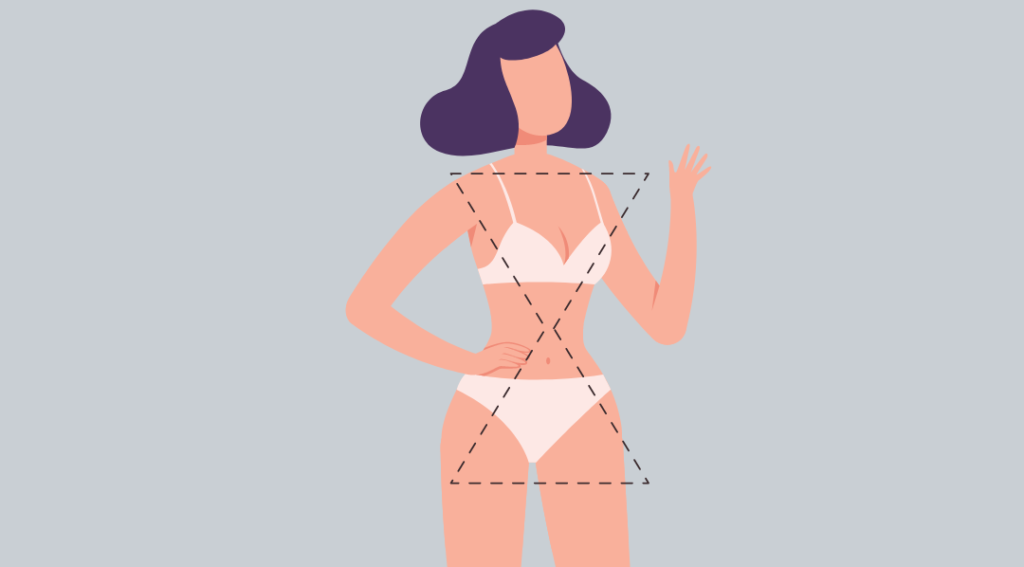
Often called the bombshell shape, the hourglass body shape is a body shape that appears to look like an hourglass because of the contoured shape of the waist, which emphasizes the wider hips and bust.
Hourglass body shape attributes:
- Your hips and shoulders have almost the exact width.
- You have rounded and tilted shoulders.
- You have a reasonably-defined waistline.
- Your buttocks are relatively rounded.
- Your lower hips are vaster than your high hips.
- Your thighs are full but slimmer than the lower hips.
- Hourglass body shapes attain weight through the hips and beyond the waist.
Health Risk :
Having an hourglass body shape means that when you gain weight, it is not concentrated in one area like apple-shaped or pear-shaped people. That means weight gain can be hard to spot if you’re not regularly checking the scale. If you become overweight, you are at higher risk for chronic diseases such as heart disease as well.
4. Apple Female Body Shape
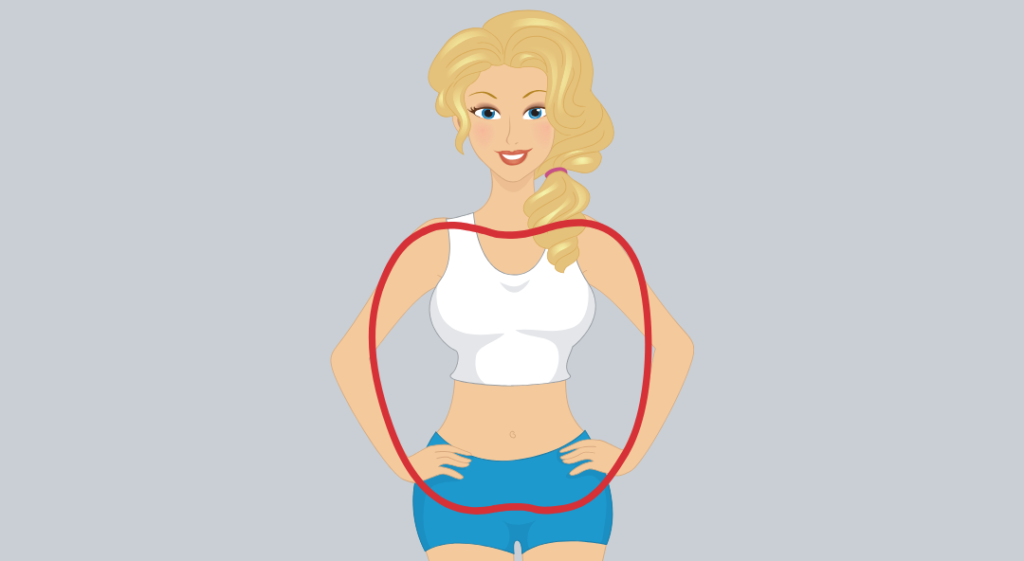
Like an apple, the apple’s body shape is determined by its rounder shape, which resembles the fruit we know. Notable signs that can be seen include a circular contour, a waist that has no definition, and equivalent body proportions. Apple body shape attributes:
- Hips and shoulders have identical widths; the waistline has an identical width or is broader.
- You acquire weight mainly around the waist, at least in balance with the other aspects of your body.
- You presumably have slim lower legs and arms.
- Your high hip is broader than your lower hip.
- Your bust and/or abdomen are bigger than your hips.
- You presumably have a shorter waist.
- Your thighs or hips are presumably the slimmest part of your body.
Health Risk :
Abdominal obesity is probably the most dangerous of all, and apple body shape is considered at the highest risk for health issues compared to the other body types. Larger waists can mean higher risk of heart disease. It can also mean higher risk of Type 2 diabetes. If you are apple-shaped but not overweight –– meaning your body mass index (BMI) is under 25 — you are still at higher risk for cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes than people with smaller waists.
5. Pear Body Shape
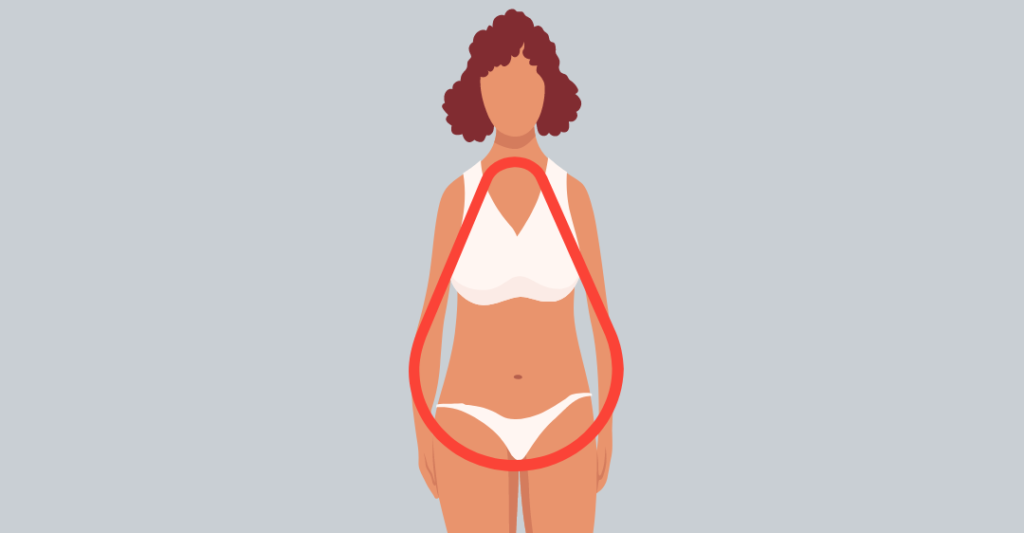
Like a pear, our last body type is called the pear-shaped body type because it resembles the pear shape with a slimmer top and a broader lower part. Pear body shape attributes:
- Your hips are broader than your shoulders.
- You have rounded, slanted shoulders.
- You have a well-defined abdomen.
- Your buttocks and thighs are well-rounded and full.
- Pear body shapes accumulate weight on their thighs.
Health Risk :
Research findings on the health hazards associated with a pear-shaped physique are inconsistent. According to earlier research, fat in the buttocks, thighs, and hips can reduce the risk of heart disease. On the other hand, a recent study demonstrates that a thinner lower body can benefit your heart more. Reducing weight in any area of your body—your buttocks, legs, or abdomen—will help lower your cholesterol if you are overweight.
Conclusion : HOW DOES BODY TYPING HELP?

A person’s body type may not be an indicator of their overall health.
Exercise – A person who seems to have an ectomorph body type may believe that they will not experience as many benefits from working out as a type that may find it easier to gain muscle, such as endomorphs. However, people with all body types will notice improvements in strength, flexibility, and weight if they follow an exercise routine to reach their goals.
Metabolic obesity – Some people may assume that certain body types are less likely to develop conditions due to being overweight or obesity. However, this is not necessarily true. Research shows that a person who has an apparently healthy, or moderate, weight can have metabolic obesity, which can lead to an increase in the risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes, ischemic heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Low amounts of physical activity, smoking, alcohol consumption, and not following a healthy, balanced diet are all risk factors of having metabolic obesity. While some genetic factors also exist, experts have not investigated this link fully. People should not assume that they are at a lower risk of developing conditions associated with obesity due to their particular body shape.
Disordered eating – A person who displays characteristics of one body shape but wants to look like another may develop poor body image issues or body dysmorphia. In some cases, a person may develop disordered eating patterns. A 2019 study investigated the effects of social media on females in college aged 18–25 years. A majority of the study participants had a healthy body mass index (BMI). However, even participants with a healthy BMI viewed their bodies as overweight compared to those of social media influencers. The researchers suggest that people who see a “thin ideal” on social media may be at a higher risk of developing disordered eating patterns in an effort to achieve this ideal.
Click on the explore button below for more info on your body shape.
